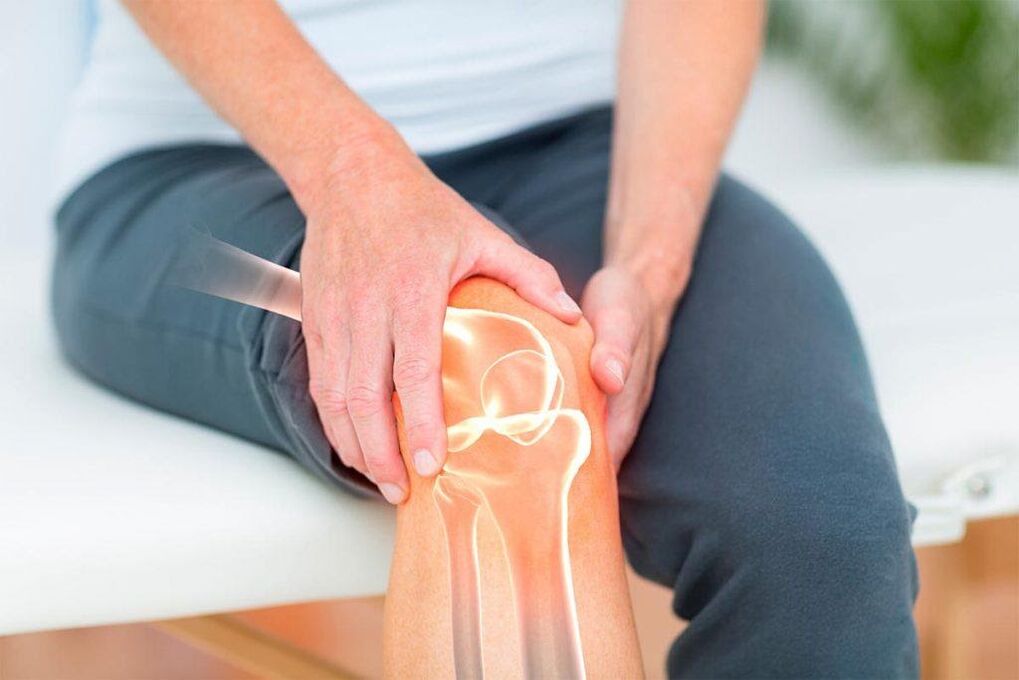
Our joints are complex and reliable mechanisms created by nature itself. Their work is invisible as long as the joints are healthy. But when they start to hurt, the world loses its former brightness. One of the most common joint diseases is arthritis and osteoarthritis. Many people confuse them, and sometimes they don’t even know what the differences are, because in both cases the joints hurt. Similar names are also misleading. In this publication, we will tell you how arthritis differs from arthrosis, about the symptoms of these diseases and methods of treatment. Despite the similarity of the names, these are completely different diseases.
What are arthritis and osteoarthritis: differences
First of all, the diseases differ in names: both have the same Latin root but different endings. You can already remember the difference between arthritis and arthrosis by the end mark. The Latin ending "-oz" means a degenerative process, destruction. The ending "-it" indicates an inflammatory process. The difference between arthrosis and arthritis is obvious: diseases have a completely different nature and course. But let’s understand in more detail what osteoarthritis and arthritis are and what symptoms accompany them.
Osteoarthritis is the result of aging and decaying joints
Osteoarthritis is a deformation and abrasion of the joint capsule that allows the joint to move easily. The disease involves structural changes, damage to cartilage, and destruction of its tissue. As a rule, arthrosis occurs after 45-50 years and is a consequence of the body's natural aging process. In the elderly over the age of 60, the disease is diagnosed in 80% with complaints of leg pain.

In young people, osteoarthritis most often develops as a post-traumatic phenomenon, for example, after fractures and bruises. It is often diagnosed in professional athletes.
Osteoarthritis often affects the joints of the knee, ankle and hip, or those that experience the greatest daily stress. Musicians often suffer from wrists and fingers. Osteoarthritis itself progresses, so the symptoms are less pronounced in the early stages.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
the main symptom is pain, which is manifested during movement and after physical exertion. As a rule, the pain in arthrosis is painful, not very strong and passes at rest, in a comfortable position;
Frequent crunching - a deep sound that results from rubbing bones;
stiffness of movement is local, only the movement of the diseased joint is disturbed;
appearance - cartilage deformation may occur, in later stages slight swelling.
Types of arthrosis
Primary - occurs as a result of the natural aging process of the joint.
Secondary - they develop in the background of trauma, as a post-traumatic manifestation.
Arthritis is a serious physical illness
While osteoarthritis is usually diagnosed in people over the age of 45, arthritis can occur at any age. As we have said, this is an inflammatory process that takes place in the joints but affects the whole body at once. The disease is associated with disorders in the immune system.
Why do joints hurt? The fact is that the immune bodies that develop in this disease attack the joints. Therefore, in arthritis, any joint can be injured: several at once or just one. Arthritis most often occurs after severe stress, anxiety, in the background of reduced immunity and hypothermia, as well as as a consequence of metabolic disorders.
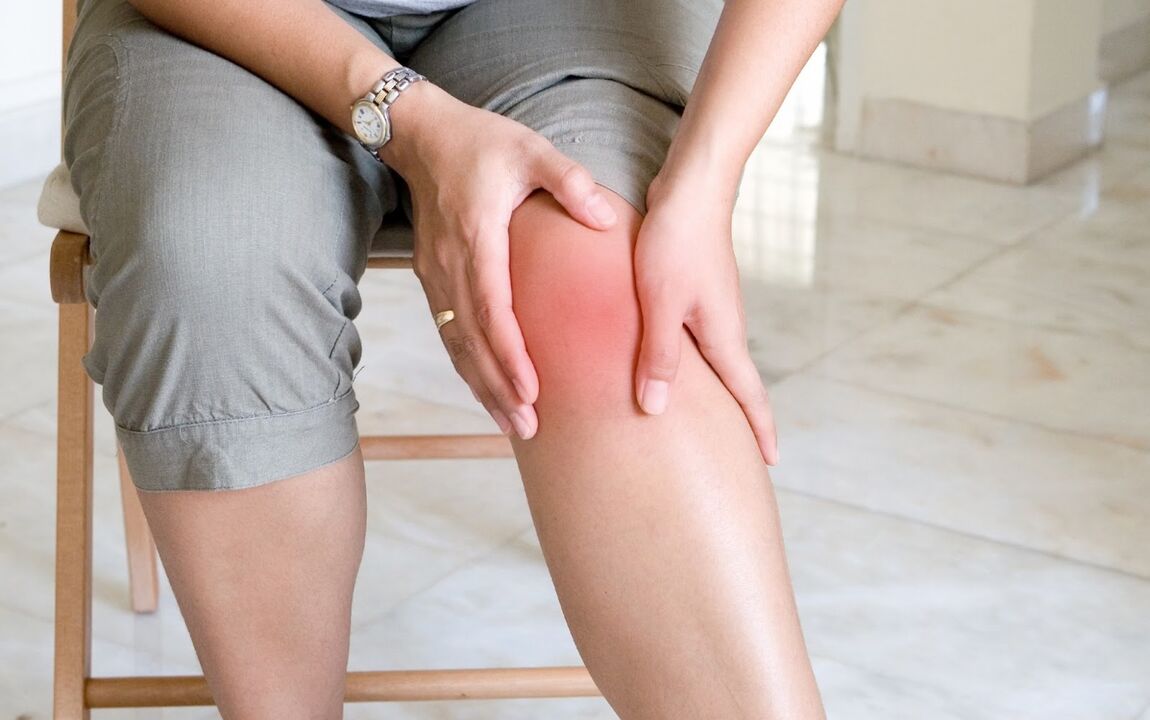

Symptoms of arthritis
pain in arthritis, unlike pain in osteoarthritis, decreases during movement but increases and becomes chronic at rest. Most often the pain intensifies at night or in the early morning hours, during rest;
joints swell, there is swelling, edema, painful palpation;
the joint area becomes red and hot;
an inflammatory reaction has been reported in blood tests;
stiffness all over the body, stiffness of movement;
the appearance of dense nodules in the area of the joints.
Arthritis is often accompanied by such manifestations:
dry eye;
weakness, chills, drowsiness;
psoriasis;
time dependence.
Types of arthritis
Depending on the nature of the disease, arthritis is divided into 2 types: inflammatory and degenerative. They are also divided into species.
Inflammatory arthritis can be:
infectious - inflammation in the joints caused by microorganisms that have entered the synovial fluid;
rheumatoid - an inflammatory process that affects the connective tissue around the joint, as well as many organs;
reactive - develops as a result of infection;
Gout is an inflammation in the joints associated with an increase in uric acid in the blood and, as a result, with salt deposition.
Degenerative occurs:
traumatic;
osteoarthritis.
Which is more dangerous: arthritis or osteoarthritis?
There is no definitive answer to this question. Because both diseases, without timely treatment, can lead to complete loss of ability to move. Osteoarthritis can be the result of arthritis. But long-term osteoarthritis can also lead to arthritis.
Treatment of osteoarthritis and arthritis: features
Pain in the joints deprives a person of the simplest joys: ordinary walks, the possibility of complete rest, freedom of movement. However, it is not always possible to recognize the alarming manifestation of this symptom in time. Often people think that this is a temporary phenomenon and try to get rid of the pain faster: self-medicate, take medication or use folk methods. But after receiving short-term relief, they do not know the main thing - the causes of the disease. Therefore, the disease worsens and takes on more severe, neglected forms.
The main recommendation of doctors is not to delay a visit to a specialist. Only a thorough examination and treatment will help avoid serious consequences. Here in the game is the ability to live and move fully.
Osteoarthritis is treated by orthopedists, neurologists and rheumatologists. The main method is to reduce the load on the diseased joint, increase the elasticity of the tissue and strengthen the muscles. In severe cases, special injections of hyaluronic acid are prescribed to help lubricate the joints, or so-called arthroplasty is performed.
However, no cure has yet been found to completely restore cartilage. Competent treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis can only stop the destruction. The main methods of treating joint disease are physiotherapy exercises and physiotherapy procedures.
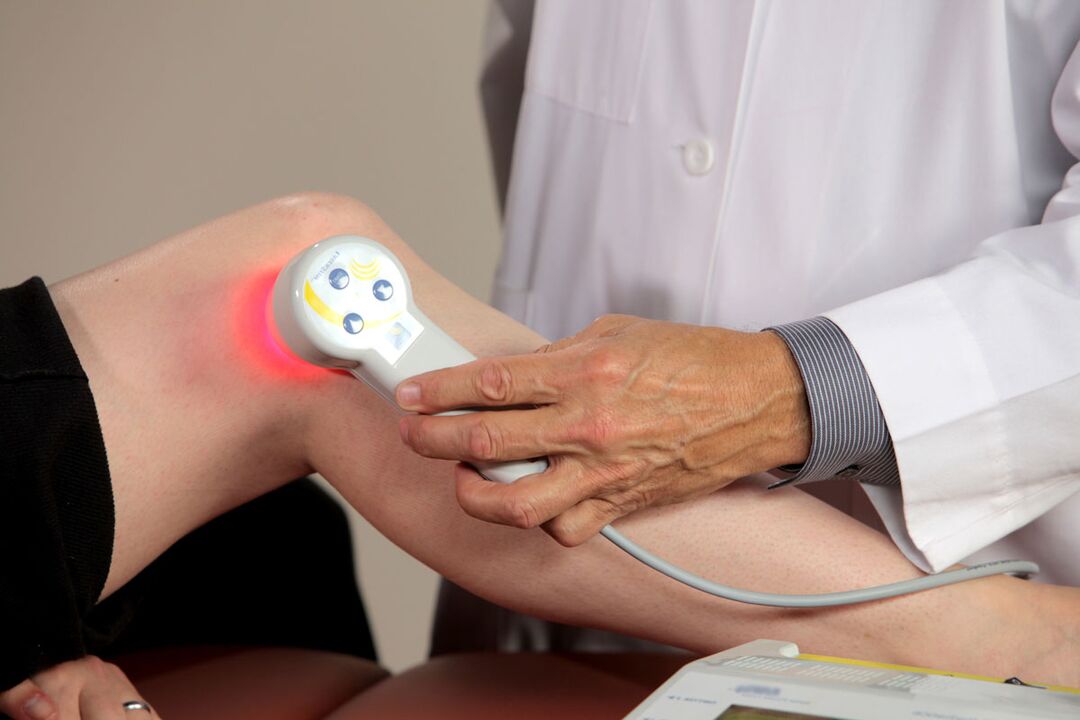
Arthritis is treated by a rheumatologist. The course of rehabilitation depends on its specific type, but it is rarely possible without special anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics. Hormonal medications are sometimes prescribed. The treatment regimen is usually as follows:
painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
physiotherapy;
proper nutrition, nutrition, restoration of metabolic processes;
drug therapy if internal organs are affected.
Prevention is the foundation of joint health
Like any disease, joint disease can be prevented. First of all, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and avoid stress.
If we consider the recommendations in particular, the experts of the clinics notice:
Weight control - in order not to overload the joints, you must always monitor your normal weight.
Moderate physical activity. They improve blood circulation, strengthen the muscular corset, which is very important for maintaining healthy joints. However, the key word here is mild, as sprains, injuries, strength exercises, and grueling sports only accelerate the process of destroying joints. Joints, swimming, cycling and Nordic walking are considered the best activities.
Properly balanced diet. As a prevention of joint disease, doctors recommend reducing the amount of red meat in the diet, as well as foods high in animal fats. But fatty fish and products containing omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, on the contrary, should be included in the menu as much as possible. Also, emphasis should be placed on fresh vegetables and fruits, in order to maintain water balance.
Wear comfortable orthopedic shoes or insoles.
Strengthen the immune system, especially avoid hypothermia and stress.
Be healthy!

























